Posted: Monday, 16 September 2024
As global water resources come under unprecedented strain, the importance of water reuse is rapidly becoming a key solution to the issue of water scarcity. With a rising population, increasing industrial demand, and the unpredictable effects of climate change, efficient water management is no longer optional—it is essential.
The Need for Water Reuse: A Global Challenge

The world's population is projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, placing enormous pressure on global water supplies . According to the United Nations, approximately 2.3 billion people currently live in water-stressed countries, a number expected to rise sharply in the coming decades . Regions such as the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Asia are already facing critical water shortages, with nations like India and South Africa experiencing significant droughts that impact both agriculture and daily life.
As the demand for water continues to grow, the future is likely to bring heightened competition between domestic, agricultural, and industrial users. The World Resources Institute warns that by 2040, over 33 countries will experience extremely high levels of water stress . This is especially concerning when factoring in the increasing unpredictability of water availability due to climate change, which is causing more frequent droughts, changing rainfall patterns, and accelerated depletion of groundwater.
In response, water reuse—or the recycling and treatment of wastewater for various applications—has emerged as a vital strategy in addressing these challenges. Proper water management, including reuse, could potentially meet up to 40% of the world’s water demands by 2030.
Technologies Alleviating Water Scarcity
Water scarcity requires an array of technological solutions that can work in tandem to provide sustainable outcomes. Several technologies have been developed to enable water reuse on industrial, municipal, and even personal levels:
1. Desalination

Desalination plants are now common in regions with access to seawater, such as the Middle East and Australia. Desalination uses reverse osmosis to convert saltwater into freshwater but can be energy-intensive and costly. However, advances in renewable energy are helping to bring down the associated carbon footprint, making it a more viable option in the future.
2. Membrane Filtration
Membrane technology, such as ultrafiltration and nanofiltration, is widely used to treat wastewater for reuse. These methods remove pathogens, suspended solids, and other contaminants to make the water fit for a variety of purposes, from irrigation to industrial processes. While effective, these systems can be expensive to implement and maintain.
3. Water Treatment Plants
Traditional water treatment plants are still vital in processing wastewater, removing contaminants through a combination of chemical, biological, and physical processes. Many modern plants now incorporate energy recovery methods to improve efficiency, but there remains a need for constant upgrades to keep pace with increasing demand.
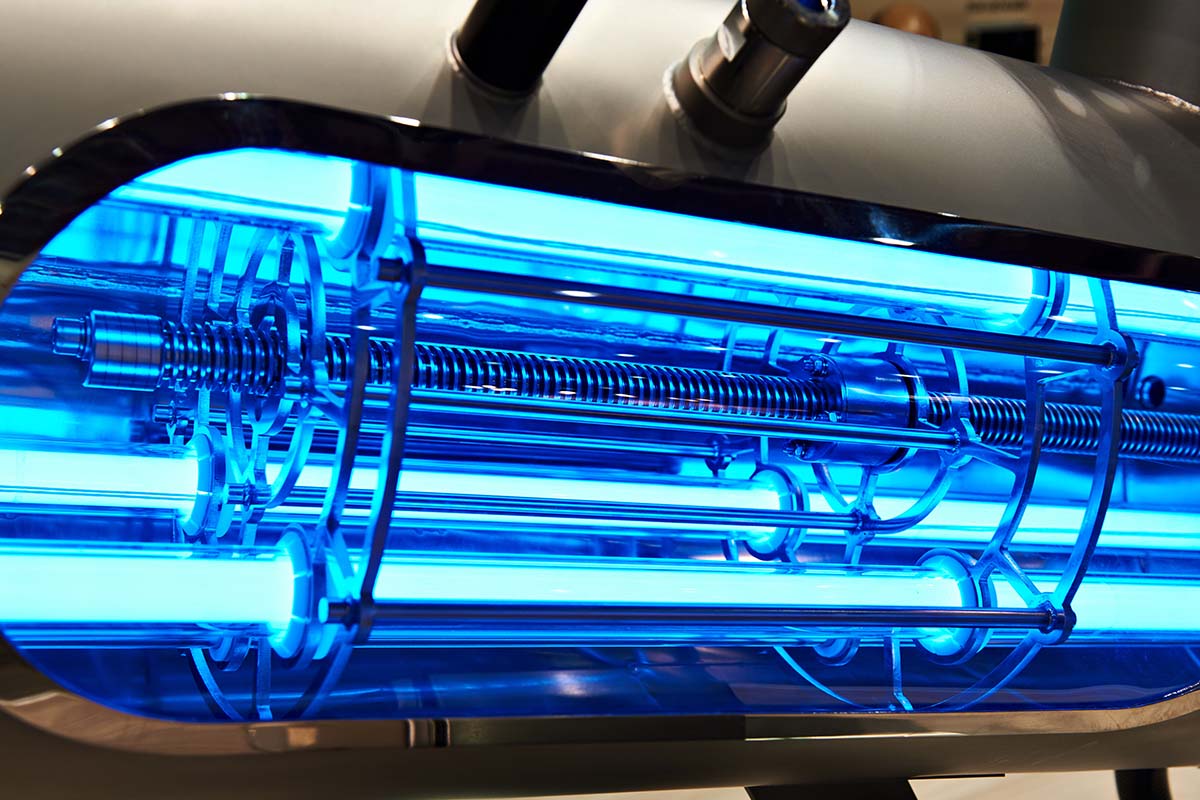
4. UV Disinfection Technology
In recent years Ultraviolet (UV) technology has emerged as an increasingly popular and sustainable solution for water treatment. Medium and low-pressure UV lamps, such as those produced by Alpha-Purify, are particularly effective in helping disinfect water by neutralising harmful microorganisms like bacteria and viruses. Unlike chemical treatments, UV disinfection leaves no residual chemicals in the water, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
UV technology is being integrated into water reuse systems globally, both in industrial-scale applications such as municipal water treatment and in smaller-scale systems designed for homes and businesses. It also has the advantage of being scalable and cost-effective, providing a critical tool in the push for water reuse.
Industrial and Personal Responsibility in Water Reuse
Water scarcity is a global problem, but its solutions require action at every level—from large-scale industrial users down to individual households.
Industrial Action
Industries that rely heavily on water, such as agriculture, mining, and manufacturing, bear a significant responsibility in adopting water reuse technologies. Closed-loop systems, where water is treated and reused within the same industrial process, are already gaining traction in sectors like oil and gas, while mining operations are beginning to adopt similar methods.
For many industries, integrating UV-based disinfection systems into their water reuse strategies not only saves water but also reduces operational costs over time by improving the efficiency of treatment processes.
Municipal and Government Actions
At the municipal level, authorities are increasingly investing in infrastructure to treat and reuse wastewater. Municipal water reuse initiatives have already been implemented in cities such as Singapore and Los Angeles, where treated wastewater is used to replenish groundwater and support agriculture . In Europe, Spain is a leader in water reuse, treating around 12% of its wastewater and employing it in agriculture and industry.
Personal Responsibility
On a smaller scale, individual actions can also contribute to water reuse efforts. From installing greywater systems that recycle water from sinks and showers to using rainwater collection tanks, households can play an active role in conserving water. Moreover, businesses and communities in towns and villages can implement local water recycling projects, contributing to regional water security.

The Role of UV Technology in the Future of Water Reuse
In summary, the global water crisis is a complex challenge, but water reuse offers a sustainable way forward. Desalination, filtration, and traditional water treatment plants will all play their part, but UV disinfection technology offers additional benefits that can compliment the other processes for water reuse systems.
Whether on an industrial scale or a personal level, UV technology provides a cost-effective, chemical-free, and reliable means of purifying water. For municipal water plants, UV can offer a complementary solution to existing methods, ensuring water is safe for both consumption and reuse. At the same time, smaller UV systems can serve communities and homes, helping to make water reuse a reality across all levels of society.
If you’re looking for advanced UV solutions to support your water reuse goals, Alpha-Purify’s range of medium-pressure UV lamps offers cutting-edge technology designed to meet both large-scale and local needs. Contact Us today for more information on how we can help you achieve sustainable water treatment.